Why are U.S. adults eating less fast food?
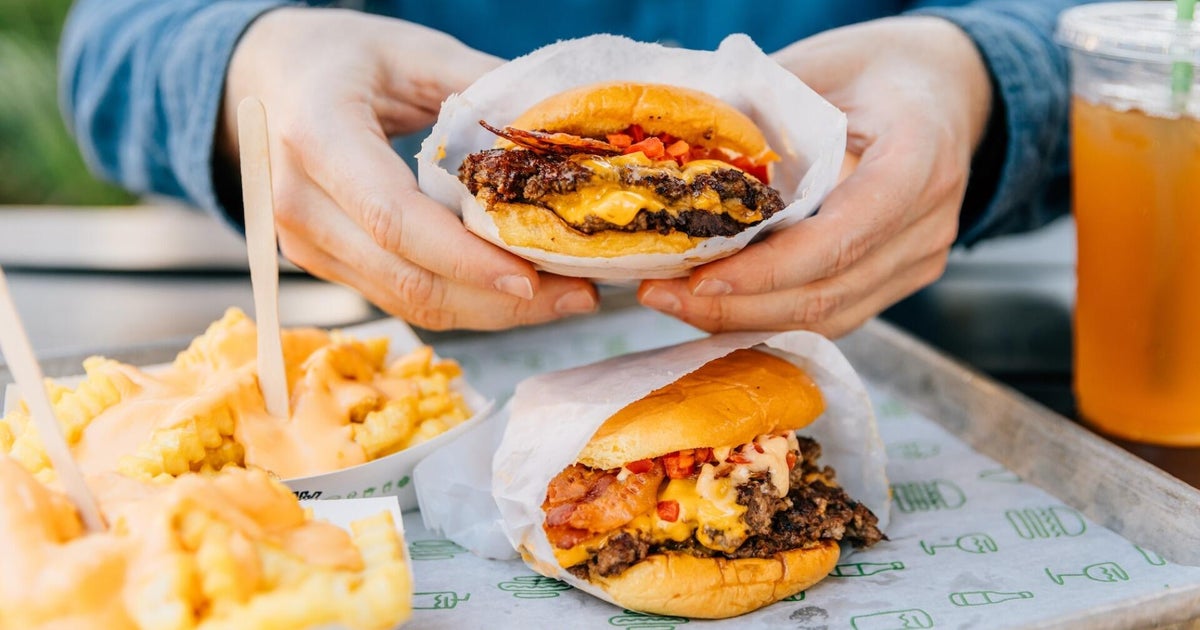 Title: Why Are U.S. Adults Eating Less Fast Food? A Healthful Report Reveals Dwindling Preferences
Title: Why Are U.S. Adults Eating Less Fast Food? A Healthful Report Reveals Dwindling PreferencesIn a recent segment of "CBS Morning News," expert Dr. Gena Hamshaw from Mount Sinai Health System discussed why fast food consumption has dropped among U.S. adults, as highlighted by the CDC's findings. This report, released in response to concerns about chronic disease risks, reveals that fast food remains one of the leading culprits in promoting unhealthy eating habits.
The Rise and Fall of Fast Food Consumption
Fast food consumption has long been a focus of public health debates. The CDC recently revealed data showing a significant decline in fast food consumption among adults over the past decade. According to their findings, fast food is often selected for its convenience, affordability, and ability to reach a broad audience, creating a double-edged sword. While it provides instant energy and nutrients, consuming too much can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
Factors Behind the Decline
The drop in fast food consumption isn't merely a statistical trend but is deeply rooted in various lifestyle factors. One major factor is dieting. Many adults consume excessive amounts of unhealthy fats, such as processed foods and sugary drinks, which contribute to weight gain and poor health outcomes. Additionally, an increasingly sedentary lifestyle, characterized by limited exercise and physical activity, has negatively impacted the consumption of fast food.
The Impact on Nutrient-Rich Meals
Fast food often prioritizes convenience and quick meals over nutritional balance. This approach leads to a diet that lacks sufficient variety in nutrients. In contrast, a balanced diet with diverse foods can support overall health and prevent deficiencies. The CDC's study underscores the importance of promoting healthier habits such as nutrient-rich meal options.
Call to Action for Change
To address this issue, public health initiatives are needed to encourage more varied and nutritious meals. This includes promoting healthy snacks, reducing sugary and processed food consumption, and advocating for better physical activity levels. By making these changes, the overall population can reduce fast food consumption while maintaining a healthier lifestyle.
In conclusion, while fast food remains an essential component of our daily lives due to its accessibility and affordability, it also poses significant health risks through nutrient deficiencies and sedentary lifestyles. A shift towards more balanced and nutritious meals is crucial for promoting public health and improving overall well-being. As Dr. Hamshaw emphasized, the CDC's findings highlight the need for comprehensive strategies to address this issue effectively.
------
Topic Live