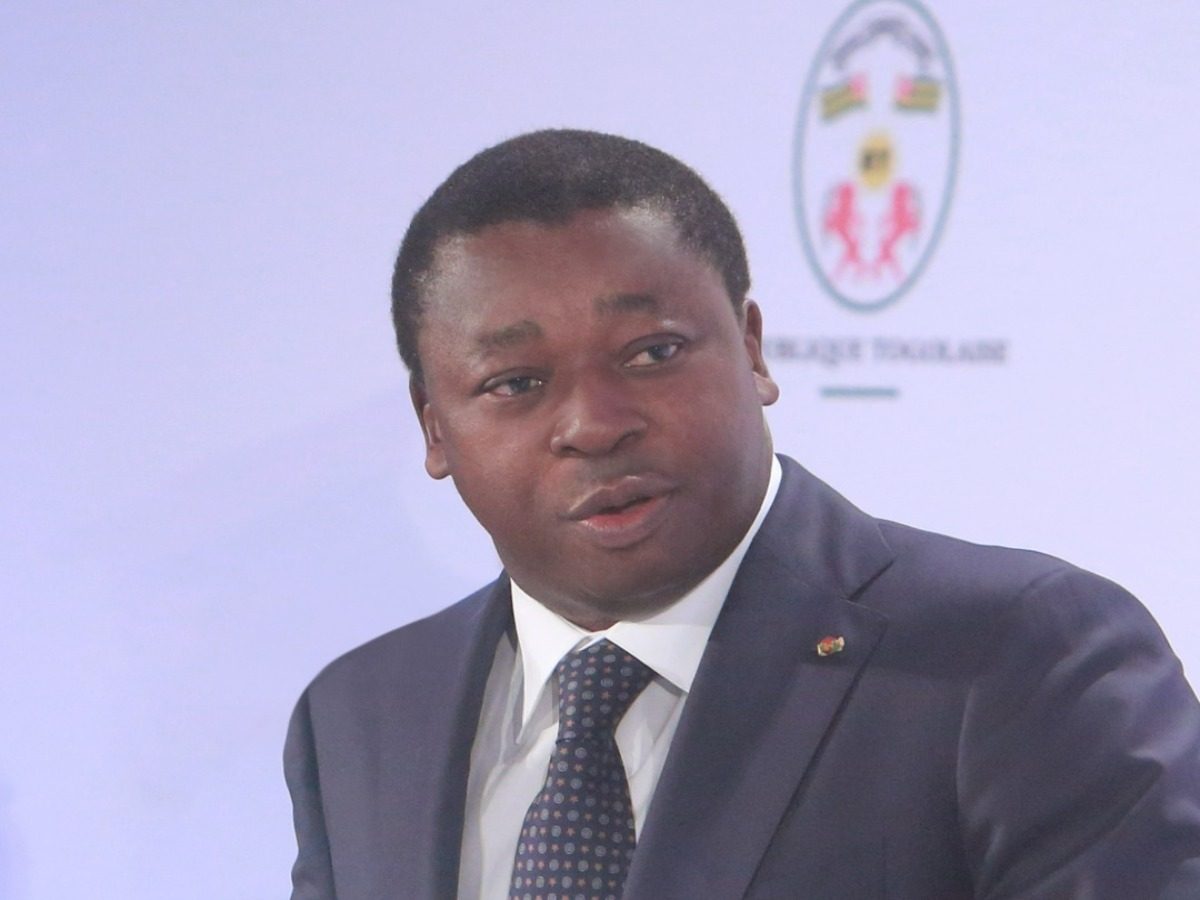
Togo’s Gnassingbé under fire as constitutional shift triggers resignation calls - Face2Face Africa
 Togo's Constitutional Crisis: An Analysis of the Rise of the Gnassingbé and the Impact on Democracy
Togo's Constitutional Crisis: An Analysis of the Rise of the Gnassingbé and the Impact on DemocracyIn Togo, a country renowned for its ethnic unity, a significant constitutional shift under President Faure Gnassingbé has sparked intense political tensions. This article explores the background of Togo's constitutional system, the implications of this change, the internal dynamics of opposition groups, and the broader societal effects.
Togo's Constitutional System and Its Significance
Togo, with its rich history of national unity, had a structured constitution that guided governance for decades. However, recent changes in Gnassingbé's leadership suggest a constitutional shift aimed at addressing issues such as economic instability and ethnic tensions. These shifts are critical because they might alter the nation's democracy, sovereignty, or political landscape.
The Controversy and Opposition Reactions
Gnassingbé's changes have sparked strong opposition reactions. The opposition, including groups like the National Movement for Unity in Togo (MNA-T), view Gnassingbé as being manipulated. They emphasize the loss of autonomy and fear of losing control over governance. Internal dynamics within opposition members are complex; some fear powerlessness, while others see a desire for stability.
The Resignation Calls and Their Timing
ResIGNATION CALLS to President Gnassingbé were made due to concerns about his power, economic instability, and ethnic unity. The calls were likely directed by opposition members, with internal discussions possibly using various methods—emails, phone messages, or meetings—and responses could vary in intensity.
Government's Response and Consequences
The government addressed the calls through formal investigations, communication with opposition leaders, and public forums. These measures aimed to regain trust and demonstrate commitment to stability. However, unresolved issues may force Togo into a reconsideration of leadership, potentially challenging future governments.
Broader Implications and Future Scenarios
Togo's political landscape could face significant changes. If resignation is not resolved, it might signal a shift toward a more democratic process or reevaluation of Gnassingbé's role. This could have far-reaching effects on the nation's governance, unity, and future leaders.
In conclusion, Togo's constitutional crisis under Gnassingbé highlights the delicate balance between democracy and stability. The rise of Gnassingbé and the ongoing tensions underscore the importance of political oversight and public engagement in navigating this dynamic situation.
------
Topic Live